Workplace safety tips
for build your own house sites
These workplace safety tips will keep the kit building site free of hazards, and low on risk. The term ‘Workplace Health and Safety’ is an area concerned with protecting the safety, health and welfare of people engaged in work or employment.
The goal of the building worksite is to foster a safe work environment for yourself, co-workers, family members, inspectors, suppliers and tradespeople entering the workplace environment. All of whom can injure themselves on the site. Before we get into the workplace safety tips, lets ask some questions and check the facts.
Why worry about Workplace safety?
If I got injured I stopped work, my time plan was shot, the missus was furious, I was off-site, and took time to heal. If someone else was injured...big problem. PL insurance is good to a point and most people accept responsibility for being a klutz, but some people get nasty when it’s not their fault. The fact is, people have the right to a safe workplace, end of story.

Workplace safety facts
One of the big risks on building sites is fatigue. Fatigued workers:
• react more slowly than usual
• fail to respond to things going on around them
• respond incorrectly
• show poor logic and judgement
• are unable to concentrate
• are less motivated and more forgetful
• have a greater tendency for taking risks
And facts from around the world..
- Each day, an average of 6,000 people die as a result of work-related accidents or diseases, totaling more than 2.2 million work-related deaths a year
- Hazardous substances kill about 438,000 workers annually, and 10% of all skin cancers are estimated to be attributable to workplace exposure to hazardous substances
- Asbestos alone claims about 100,000 deaths every year and the figure is rising annually
- Each year there are at least 60,000 fatal accidents on construction sites around the world
- One in every six fatal accidents at work occurs on a construction site
- In industrialized countries, as many as 25% to 40% of work-related deaths occur in on construction sites, even though the sector employs only 6% to 10% of the workforce
- In some countries, it is estimated that 30% of construction workers suffer from back pains or other musculoskeletal disorders

Workplace safety hazard assessment
Hazard analysis or hazard assessment is a process in which individual workplace hazards are identified, assessed and controlled or eliminated as close to the source (location of the hazard) as reasonable and possible. So on a building site there are many potential hazards:
~Mechanical hazards: equipment, tools, falls, trips, entanglement and being struck by objects
~Physical hazards: noise, electricity, heat, cold and vibration
~Biological hazards: bacteria, virus, fungi and mould
~Chemical hazards: fuel, acid, particulates, fumes and fire
Kit builder workplace hazards
Some
of the workplace hazards I encountered on my site included noise from the
generator, my hammer drill, speed saw and fibro cutter, working at height
on ladders, on framing and on roofing, working all day in the sun,
getting injured by the equipment I was using, having things fall on me
and tripping over nearly everything.

The terminology used in WHS varies, but generally speaking:
A
hazard is something that can be eliminated or controlled. A risk is a
combination of the probability that a particular uncontrolled hazard can
cause harm and the severity of the harm involved. A Risk Assessment should identify the hazards, evaluate the risk and identify and prioritize appropriate control measures.
Definition of risk management
Policies, procedures, and practices involved in identification, analysis, assessment, control, and avoidance, minimization, or elimination of unacceptable risks.
Workplace safety tips to keep your site safe
- Plan to and keep your site clear of waste, clutter, chords, off-cuts and general rubbish
- Prepare and or build clear paths, entries and ramps to frequently used work areas
- Utilise gantries, scaffolding, ropes to anchor points, safety harnesses and guardrails
- Use well maintained tools and equipment, discard damaged equipment
- Use dust collectors on cutting equipment
- Ensure ladder safety by bracing ladder footings and tying off to reduce slippage
- Use well known sun safety tips such as wearing a decent hat, using sunscreen and wearing a long sleeved shirt
- Use hazard symbols/signs, safety posters and especially bio hazard signs
- Wear appropriate safety gear when operating equipment e.g. gloves,
masks, prescription safety glasses, ear plugs, face shields, solid boots
etc
- Have a well equipped first aid kit in an accessible place
- Keep a mobile phone handy and put the emergency number on speed-dial
- Have fire safety protection equipment on-site: extinguisher and blankets are a minimum
- Formulate a site specific safety plan and checklist for your building site
These workplace safety tips may seem obvious, but as a site foreman or woman, you are morally and legally bound to utilise them and do your best to create a site specific safety plan. Remember, frequent hazard assessments and risk assessments will make health occupational safety a standard.
Job safety analysis
If a worker you are responsible for injures themselves on your worksite, and makes a claim for workers compensation, the insurance company will need to investigate all of your safety devices, written procedures, signage and hopefully your job safety analysis of the task that led to the injury. This will limit the premium rise the insurance company will enforce if the claim is approved.
JSA Steps
1. Document the activity: write down the tasks that make up the activity, step by step.
2. Identify the hazards: identify what part of the task may cause injury to those doing the work or to anyone else nearby.
3. Document the control measures: for each identified hazard, list the measures that need to be put in place to eliminate or minimise any likely risk of injury to those involved.
4. Identify who is responsible: document the name of the person responsible for implementing the control measure.
5. Monitor and review: make sure the activity is supervised to ensure the documented process is being followed.
Safety slogans for your site
Building sites need to be safe. Catchy safety slogans; which have a ring to them, are one of the best ways to get that information across. Work slogans can change the face of the workplace, the attitude of workers and the way workers go about their work, even in minor ways.
Choose one or many of these safety quotes and make into your own signs and get them visible about the kit home workplace.

- There's no face like your own, wear face protection
- Safety rules are your best tool
- Safety glasses: All in favour, say "Eye!"
- Move your ladder to avoid reaching
- Hearing protection is a sound investment
- Hard hats, they're not just for decoration
- Hand in, hamburger out
- To avoid a scene, keep your workplace clean
- Eyes are priceless, eye protection is cheap
- Don't let the light go out, wear eye protection
- Don't be a fool. Use the proper tool
- Forgot your hearing protection? Forget about hearing
- Safety saves, Accidents cost
- Safety First, Avoid the Worst
- Hug your kids at home, but belt them in the car!
- Safety is like a lock - But you are the key
- Tomorrow - Your reward for working safely today
- Safety rules are your best tools
- Safety fits like a glove; Try one on
- Safety...Do it. Do it right. Do it right now
- Lifting is a breeze when you bend at the knees
- Business stalls if you slip and fall
- Lead the way, safety today
- Save tomorrow. Think safety today
- Wear safety shoes and keep a good footing on life
- While on a ladder, never step back to admire your work
- Slip, trip and fall are four-letter words
- This tool will punch you in the face , if you let it
Add your safety slogans to placards, site signs, walls near machinery and tools, even to your own vehicles and trailers. With the soaring price of insurance premiums and the fact that work cover is really a 'loan' if you claim i.e. you have to pay it back through higher premiums, work slogans can be a money saver in the long term while building your kit home.
Workplace safety tips: sun safety

These sun safety tips will keep you alive, or at least stop part of your face falling off from the effects of the sun, while building your kit home. Teaching sun safety to our kids is relatively easy, but we struggle to apply those 'safety in the sun' principles, which we demand from them, to ourselves on site.
Sun Safety Tips
- Use a broad-spectrum, high sun-protection factor sunscreen, at least SPF 30+
- Apply your sunscreen at least 20 minutes before going outside, and reapply at least every 2 hours
- Apply a protective lip balm. They are easy to store on your pocket and easy to apply
- Wear protective clothing including long sleeves and a collared shirt. Loose, lightweight clothing that covers as much skin as possible is best
- Get a broad-brimmed hat that is comfortable and doesn't impede your forward view
- Buy yourself some good safety sun glasses. Choose sunglasses that filter out UVA and UVB rays; large, close-fitting wrap-around styles offer the best protection because they reduce glare and reflected UV radiation
- Seriously consider renting/borrowing/buying a small marquee or shade sail to cover frequently used areas such as your saw bench or tool trailer
- Provide shade for workers/tradies to have 'out of sun' breaks
- Once the roof is on, do as much under-roof work as possible
- If working on the roof, use a bandana, face covering and a large hat.
- Just because you have applied suncreen doesn't mean you should extend your time in the sun
- You should also keep to the shade and stay out of the sun in the middle of the day
- Surfaces such as water, sand and concrete reflect ultra-violet rays — you may end up with sunburn even if you are seated in the shade
- Check with your doctor or pharmacist regarding medications you use that may increase your sensitivity to sunlight
- Teaching sun safety to your site workers might seem childish, or not your problem, but setting your face up for the scalpel is a bad decision, all for the sake of comfort.
Click here to download a PDF publication on Sun Safety at Work
Ladder safety
Ladder safety for owner builders is an obvious WHS issue and can minimise serious injury on your site. Less than a two metre fall can be dangerous and many serious accidents from ladders are from short falls. As ladder jobs are frequent in this game, here are a number of great tips to keep safe while getting up high.
Do's
1. Always work within arm's reach of the task
2. Always stop before the second last step of the ladder
3. Place the ladder on firm dry ground or use leveling/stabilising devices.
Dont's
1. Don't walk the ladder, climb down and reposition
2. Don't use a ladder in wind and or rain
3. Don't use a ladder whilst using medication that effects balance
4. Don't allow a second person on the ladder at the same time
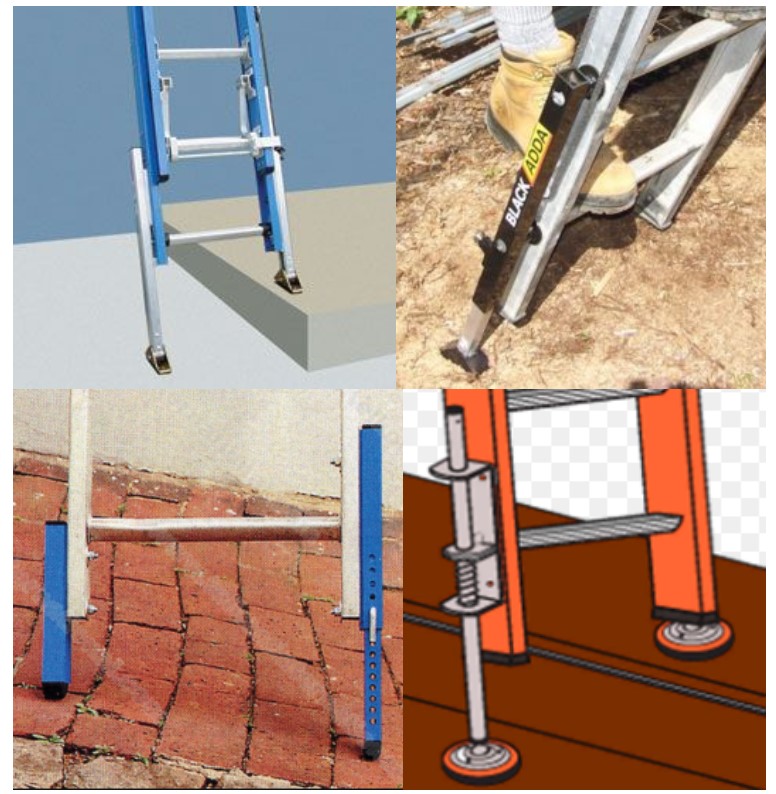

Stabilising devices
A constant hazard of ladder use is the feet of aluminum extension ladders slipping backward away from the wall or sinking into the earth. There are a number of 'ladder stabilizers' available that spread the weight of the ladder feet and anchor them to prevent movement.
Levelling devices
Is there ever a level surface for a ladder? Mostly the surface will be sloped, both left to right and forward to rear.
Using a 'leveliser'- a purpose made triangular device, eliminates the need for finding the right width piece of offcut to raise the lower foot of your ladder. A modern aluminium ladder, sometimes called a safety ladder, may have slide out extensions that can be fixed to the lower level side. Other products are stand alone attachments: see pic provided.
Standoff devices
Tasks such as painting walls, working on gutter systems, soffits, high windows etc, require a 'stand off' device so the top of the ladder doesn't sit against the wall, gutter or window. Special roof ladders or scaffold ladders have securing devices and extra bars at the top to provide safe egress and entry to the ladder at height.
Fall arresting systems
If you choose not to use a scaffold, ladder work for second storey tasks can be rather dangerous. Fall protection systems such as ladder securing safety belts, lanyards and harnesses are available to maintain safety at height.
I have touched on the basics here, but for more in depth ladder safety information and resources, download the excellent and 'free' Ladder Safety Training resource on the Complianceandsafety.com website.
Return to Home building plans or home